AI is deemed to be the new superpower. Adoption of AI in various capacities is at 72% across industries, world wide, according to one study, and it does not show signs of slowing down. Meanwhile, concerns around ethical issues surrounding AI are also high – according to a PEW research report published in April 2025, more than 60% of the general public polled voiced concerns around misinformation, security of their data, and bias/discrimination.
We, as database technologists and software developers, are an important part of this evolution – A github research survey from 2024 indicated that more than 97% of respondents were using AI for coding already. Many of us may also be involved in developing AI based software in various forms.
But how aware and conscious are we of ethical issues surrounding AI? Granted, our usage of AI may be driven by work related reasons, but what about our own personal stances? Are we aware of ethical issues and do ethical issues factor into what we think of AI in any way?
Studies reveal that developers show only moderate familiarity with ethics frameworks such as fairness, transparency, and accountability. According to a survey of 874 AI incidents in 2025, 32.1% of the developer participants had taken no actions to address ethical challenges. (Zahedi, Jiang, Davis, 2025). Another study in 2024 proved the need for ‘comprehensive frameworks to fully operationalize Responsible AI principles in software engineering.’(Leca, Bento,Santos, 2024).
The purpose of this blog post is to look at ethical concerns related to AI as expressed by developers, in the Stack Overflow Developer Survey, 2024. Using this dataset, I looked into research questions as below :
1.How do ethical issues with AI, expressed by developers, correlate to their stances on AI?
2.How do productivity gains correlate to developer stances on AI?
3.How does productivity as a gain change the correlation of ethical issues on the stance of AI?
4. How does bias as an ethical issue and age of the developer relate to the stance of AI?
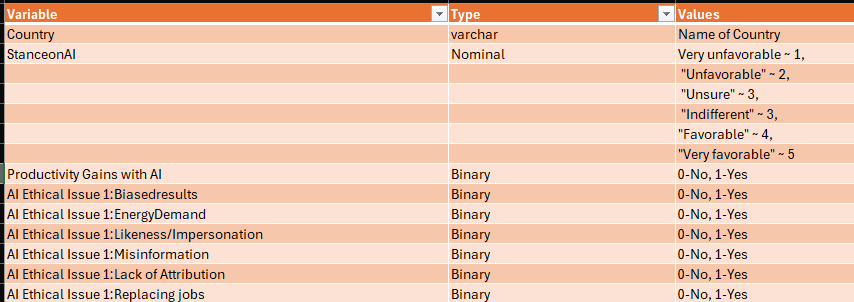
The dataset has 41,999 observations (after cleansing for those under 18 and those with no stances on AI) across developers in 181 countries. After the transformations, it looks like below.
Methodology (this may make sense if you are stats savvy. Feel free to skip it if not.)
The outcome variable on AI stance is a nominal one with increasing order. This is a dummy variable created based on verbiage based responses in the original. The gap between each level is assumed to be the same, although it may not necessarily be.I’ve used the POLR function in R, because it models cumulative log odds as opposed to a coefficient with multinom.I have used odds ratios and probability to explain findings as they are simple and easy to understand.
Descriptive Statistics of the dataset
Top ten countries with respondents are as below, with the US having significantly high # of people. This may be due to the fact that the US has significantly high number of developers in general. It also means views overall maybe skewed largely in favor of US respondents. For this analysis, I have not filtered the dataset by country, although that maybe something worth doing as the next phase.

Stances on AI were overwhelmingly positive with nearly half the respondents (48.2%) rating it as most favorable. Just 1.2% rated it as very unfavorable, with the rest being in between.

65% of respondents reported productivity gains with AI.

. There were a total of six ethical concerns – biased results, misinformation, lack of attribution, energy demand, impersonation or likeness and likelihood of replacing jobs without creating more jobs. (Some more were too custom to be included for analysis). . The majority of respondents had more than one ethical concern. Misinformation(25.8%) and lack of attribution(21.03%) ranked highest among the concerns. Very few respondents (2.11%) had no ethical concerns.

Research Question 1: How do ethical issues with AI, expressed by developers, relate their stances on AI?
1 I decided to group all the ethical concerns and weigh them against stance. This is because most respondents have multiple concerns.
2 I also verified if concerns overlap (ie impact of one concern is taken care of by another) – a term in statistics called ‘multicollinearity’). This was not the case, as demonstrated by the image below. (Values on the boxes are very small compared to 1).

3 The results of the analysis were as below.

Data Source: 2024 Stack Overflow Developer Survey
Odds are the ratio of an event happening to its not happening. In our case, the ‘event’ is a possibility of a lower stance. Except for biased results, all other ethical concerns show odds of less than 1, which means a less favorable stance. Even with biased results, there is only a slight increase in stance and that maybe related to other factors we have not considered. Energy demand seems to have the highest correlation to lowered stances.
Research Question 2: How does productivity as a gain relate to the stance of AI?
Predicted probability is the chance of an event (in this case a change in stance on AI) happening out of all possibilities. The graph shows chances of a high stance (4 or 5) have a high percentage of probability with higher productivity gains (tall green bars). But, it also shows that those stances are taken by those with no productivity gains (red bars are high too for stance 4, although not very high for stance 5). A lot of people with no productivity gains show a moderate stance (tall red bar with 3).

Data Source: 2024 Stack Overflow Developer Survey
Research Question 3: How do ethical issues and productivity as a gain relate to the stance of AI?
This question is about examining how stances on AI change with both ethical issue and productivity factored in. Out of the six ethical issues, I chose two – concerns around bias and misinformation. The charts are as below, and were mostly similar.
Data Source: 2024 Stack Overflow Developer Survey
From these graphs, we can infer that
All things being equal, those with gains and concerns (red bar) show highly favorable stances (4 or 5).
All things being equal,those with gains and no concerns (green bar) also show neutral to favorable, but not highly favorable – perhaps other factors related to usage maybe in play here.
All things being equal,those with no gains and concerns seem moderate to favorable, with some less favorable also. (blue bar).
All things being equal,those with no gains and no concerns seem to lean neutral to favorable. (purple).
Overall, productivity gains appear to show more favorable stances (green and red bars).
Research Question 4: How does bias as an ethical issue and age of the developer relate to the stance of AI?
Adding age to bias as an ethical issue and analyzing it with stances on AI reveals below.

Source: 2024 Stack Overflow Developer Survey
All things being equal,The odds of people in the oldest age bracket (over 65 years old) taking a less favorable stance seem significantly higher compared to the youngest age bracket of 25-34 years old.
Findings and future work
Majority respondents have expressed ethical issues.
Energy Demand as a concern appeared to have the highest correlation to less favorable stances.
All other ethical issues had a correlation on less favorable stances except bias.
Productivity gains seemed associated with higher stances despite ethical concerns.
Bias as a concern and misinformation as a concern do not seem to impact higher stances significantly.
Favorable stances seem to be high overall , regardless of productivity or ethical issues.
Limitations
It is important to bear in mind that correlation <> causation, and that favorable or less favorable stances do not necessarily have to reflect ethical concern or lack of it. But given the patterns found, it is worth researching further for possible relations to demographics (country, age), and also filtering the dataset by specific countries for more insight.
The dataset is also limited to developers, not developers working on AI specifically, although some of them may be. Perspectives and findings may vary with a dataset of AI Developers.
The dataset is also skewed heavily in terms of respondents from USA compared to other countries.
Resources on Responsible AI
Below are some resources on responsible AI, which has to be the concern of every person using it.
Online Courses & Certifications
AI Ethics by the Linux Foundation (LFD117x)
Responsible AI by Microsoft
Books
‘Artificial Unintelligence’ by Meredith Broussard
‘Ethics of Artificial Intelligence’ by S Matthew Liao
‘Atlas of AI’ by Kate Crawford
Academic & Organizational Frameworks
https://datamodel.com/responsible-and-ethical-ai-frameworks/ (blog post by Karen Lopez, InfoAdvisors, with a link to several resources)
References
S. T. (2025, May 6). AI Insights: 20 statistics transforming business in 2025. Https://Blog.Superhuman.com/Ai-Insights/. Retrieved July 1, 2025, from https://blog.superhuman.com/ai-insights/
Mcclain, C., Kennedy, B., & Gottfried, J. (n.d.). Views of risks, opportunities and regulation of AI. http://Pewresearch.org. https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2025/04/03/views-of-risks-opportunities-and-regulation-of-ai/
Daigly, K., & G. S. (n.d.). Survey: The AI wave continues to grow on software development teams. http://Github.Blog. https://github.blog/news-insights/research/survey-ai-wave-grows/
Värttö , A. (2025). Awareness of AI Ethics in Professional Software Engineering: A survey [Master’s thesis, University of Oulu]
Gao, H., Zahedi, M., Jiang, W., Lin, H. Y., Davis, J., & Treude, C. (2025). AI Safety in the Eyes of the Downstream Developer: A First Look at Concerns, Practices, and Challenges.
Leça, M. D., Ben to, M., & Santos, R. D. (2024). Responsible AI in the Software Industry: A Practitioner-Centered Perspective. ArXiv. https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.07620ArXiv. https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.19444